Fintech – the short form for financial technologies is creating a lot of noise both in the digital and physical world. In fact, according to Tech Crunch, global tech funding in 2022 was $75.2 billion, 52% more than the amount invested in 2020. With the rapidly increasing developments in fintech, companies, and organizations must brace themselves to benefit from fintech app development.
From understanding market trends to ensuring compliance and user experience, we will delve into the critical steps and considerations that can help you build successful FinTech apps. Get ready to discover the exciting world of fintech app development and unlock new possibilities in the financial industry.
This guide will shed light on the following points:
- What is fintech app development?
- How to build a fintech app?
- What are the challenges associated with fintech app development?
- Importance of fintech apps overall
What is Fintech App Development? Types and Features to Know
Fintech app development refers to creating mobile or web applications that provide financial services using innovative technologies. These apps typically offer functionalities such as:
- mobile banking
- online payments
- investment management
- budgeting tools, and more.
Key Features of Fintech Apps
To meet the financial industry’s needs, fintech apps should or tend to have the following features:
- Account Management: To allow users to create and manage their accounts.
- Payments and Transfers: To facilitate seamless and secure payment transactions.
- Mobile Banking: To provide banking services on mobile devices, enabling users to perform tasks such as depositing checks, applying for loans, managing investments, and accessing financial statements.
- Budgeting and Expense Tracking: To help users track their expenses, set budgets, and monitor their financial health. These features may include categorizing expenses, generating spending reports, and providing insights into saving and budgeting habits.
- Investment and Wealth Management: To provide investment platforms, allowing users to invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or other investment instruments.
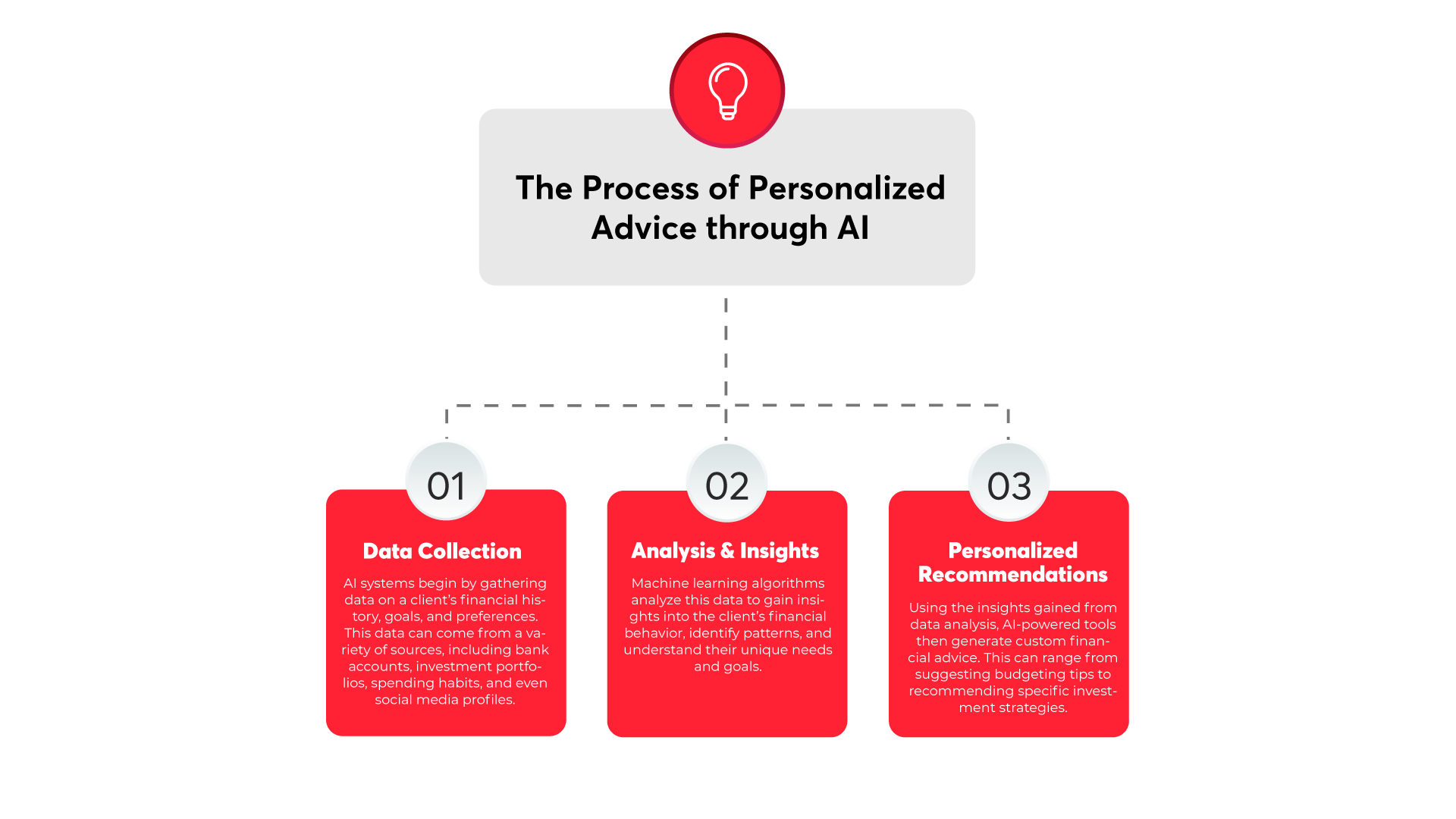
- Personalized Recommendations: To analyze user data and provide personalized financial recommendations by leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms. This can include tailored investment options, savings plans, or financial product and service suggestions.
- Security and Fraud Protection: To prioritize security measures to protect user data and prevent fraud. They may include features such as two-factor authentication, biometric authentication (e.g., fingerprint or face recognition), transaction monitoring, and real-time fraud alerts.
- Integration with Third-Party Services: To integrate with external services such as payment gateways, financial institutions, or budgeting tools. This enables users to link their accounts, access financial data, and perform transactions within the app.
- Notifications and Alerts: To inform users about their financial activities through real-time notifications and alerts. These include transaction updates, account balance changes, payment reminders, and upcoming bill due dates.
- Customer Support and Chatbots: to provide customer support features, including in-app or AI-powered chatbots. These features allow users to seek assistance, ask questions, or resolve issues related to their accounts or transactions.
What are the key considerations when building a fintech app?
When building a fintech app, one must consider the following factors:
- Security: Since fintech apps handle sensitive user data, it is crucial to implement robust security measures and protect user data from unauthorized access, breaches, and fraud.
- Compliance: It is important to clearly understand relevant regulatory frameworks (e.g., data protection, anti-money laundering, Know Your Customer) and ensure that the app is designed and developed in compliance with these regulations.
- User Experience (UX): Providing a seamless and intuitive user experience is paramount when planning to build a fintech app. It is important to remember that the app should be easy to navigate, with a user-friendly interface and intuitive design.
- Integration with Financial Systems: Fintech apps often require integration with external financial systems, such as banking APIs, payment gateways, or investment platforms. Ensuring smooth and secure integration with these systems is essential for providing reliable and accurate financial services. APIs and secure data exchange protocols should be implemented to facilitate seamless integration.
- Scalability and Performance: As user bases and transaction volumes grow, the app should be capable of handling increased traffic and processing transactions efficiently.
- Data Privacy and Consent: Implement privacy features such as explicit consent mechanisms, transparent data usage policies, and the ability for users to control their data. Compliance with data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), should be a priority.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are crucial in developing fintech apps. Thoroughly test the app for functionality, security, and compatibility across different devices and platforms. Performance testing of the app is also necessary under several conditions. Conduct both manual and automated testing, and consider employing external security audits or penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities.
- Continuous Improvement and Updates: Fintech is a dynamic field, and it is important to iterate and improve the app over time. Monitor user feedback, track analytics, and stay updated on emerging technologies and industry trends to introduce new features, enhance security, and address user needs through regular updates and releases.
Types of Fintech Apps
Now that we have discussed the major features of fintech apps, we can discuss their categories. The major types of Fintech apps include:
- Mobile Banking Apps: include features such as balance inquiries, transaction history, fund transfers, bill payments, and account management functionalities.
- Payment and Wallet Apps: facilitate digital payments and act as virtual wallets, allowing users to make payments, send money to peers, split bills, and store payment information securely. PayPal and Google Pay are prominent examples.
- Personal Finance and Budgeting Apps: assist users in managing their finances, budgeting, and tracking expenses. They provide features like expense categorization, financial goal setting, spending analysis, and savings management.
- Investment and Wealth Management Apps: cater to users interested in investing and wealth management. Users can track portfolios, perform investment analysis, check real-time market data, and get personalized investment recommendations.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending Apps: connect borrowers with individual lenders, bypassing traditional financial institutions. They provide a platform for users to borrow money or invest in loans directly.
- Insurance Technology (InsurTech) Apps: focus on digitizing and streamlining insurance processes. They offer features such as policy management, claims filing, insurance comparison, and personalized insurance recommendations. Examples include Lemonade, Policygenius, and Oscar Health.
- Cryptocurrency Apps: Cryptocurrency apps enable users to buy, sell, and manage cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc. Binance and Coinbase are some of the most popular crypto apps and provide features like cryptocurrency wallets, price tracking, trading platforms, and secure transactions.
- Financial Aggregators: consolidate financial data from multiple accounts or institutions into a single platform, allowing users to view a comprehensive overview of their financial situation. They often provide account aggregation, spending analysis, and personalized financial insights. Examples include Mint, Personal Capital, and Clarity Money.
- Digital Payment Solutions for Businesses: These fintech apps cater to businesses by offering digital payment solutions, invoicing tools, payment gateways, and merchant services. Businesses can send and receive online payments and manage invoices with such solutions. Stripe and PayPal for Business are popular examples of such solutions.
Fintech App Development Process
The process to develop a fintech app comprises the following steps:
Define Your App’s Purpose and Target Audience:
To develop a fintech app, you must have a purpose in mind; what problem should your app aim to solve? What value will it provide? Who will be the target audience? Ask these questions and define your target audience by understanding their needs, preferences, and pain points.
Conduct Market Research:
Market research is an integral part of any process. Start by analyzing the existing market landscape and competition and determining whether or not your fintech app can succeed in its purpose. Check the potential opportunities as well as risks and challenges. Apprise yourself of the market trends and if your goal aligns with them.
Plan and Design:
The design part requires outlining the app’s features, functionality, and user flow. After that, the design team works on creating wireframes or prototypes to visualize the app’s structure and user interface (UI). The focus has to be on making an intuitive and user-friendly design rather than relying primarily on aesthetics. A professional UX design service can assist you in this step.
Backend Development:
The functionality and infrastructure rest on the backend, especially since it involves developing the APIs and integrating the necessary third-party services. To ensure data protection, robust security measures and encryption protocols must be implemented during backend development. This includes user authentication, transaction processing, account management, data encryption, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Frontend Development:
Frontend development comprises the design and development of the user interface (UI). The UI must be responsive and optimized to fit multiple screen sizes and resolutions. Also, core features of the app, such as user registration and authentication, account management, transaction processing, or data visualization, are implemented during front-end development.
Test and Quality Assurance:
Once the front and backend have been developed, the application must undergo thorough testing to identify and resolve bugs, errors, and usability issues. Make sure to perform different types of software testing such as functional, integration, security, etc.
Compliance and Security:
- Ensure compliance with relevant regulations such as AML, KYC, and data protection laws.
- Execute strong security measures, encryption protocols, and user authentication mechanisms.
- Conduct security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities.
Deploy and Release:
Finally, now that the app has been designed, developed, and tested, it is time to prepare it for deployment. Following the platform-specific guidelines, create developer accounts and submit the application for review. Make sure to address any issues that arise during the release process from the app store or the web hosting provider.
Continuous Improvement and Maintenance:
Continuously monitor user feedback and analytics to gather insights for future updates and enhancements. Regularly release updates to fix bugs, introduce new features, and improve performance. Since new technologies arise every now and then, stay updated with the industry trends to ensure the app remains competitive and relevant.
Technologies Used in Fintech App Development
The tech stack that goes into building a fintech app entails:
- Programming Languages such as Java, Swift, JavaScript and Python.
- Mobile App Development Frameworks such as React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin.
- Backend Development Technologies such as Node.js, Ruby on Rails, and Django.
- Cloud Platforms and Infrastructure such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- APIs and SDKs, which further include:
- Payment Gateways
- Banking APIs
- Financial Data APIs
- Database Systems:
- Relational Databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, or Microsoft SQL Server for structured data storage and retrieval.
- NoSQL Databases such as MongoDB, Cassandra, or Firebase.
- Security and Authentication through
- Encryption, which comprises utilizing encryption algorithms and protocols like SSL/TLS for secure data transmission and storage.
- OAuth and OpenID Connect: Industry-standard protocols for secure user authentication and authorization.
- Biometric Authentication: Integration with fingerprint scanners or facial recognition technologies for secure user authentication.
- Data Analytics Tools such as frameworks like Apache Spark or Hadoop for big data processing and analysis.
- Machine Learning Libraries such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, or scikit-learn for developing machine learning models for tasks like fraud detection, risk assessment, or personalized recommendations.
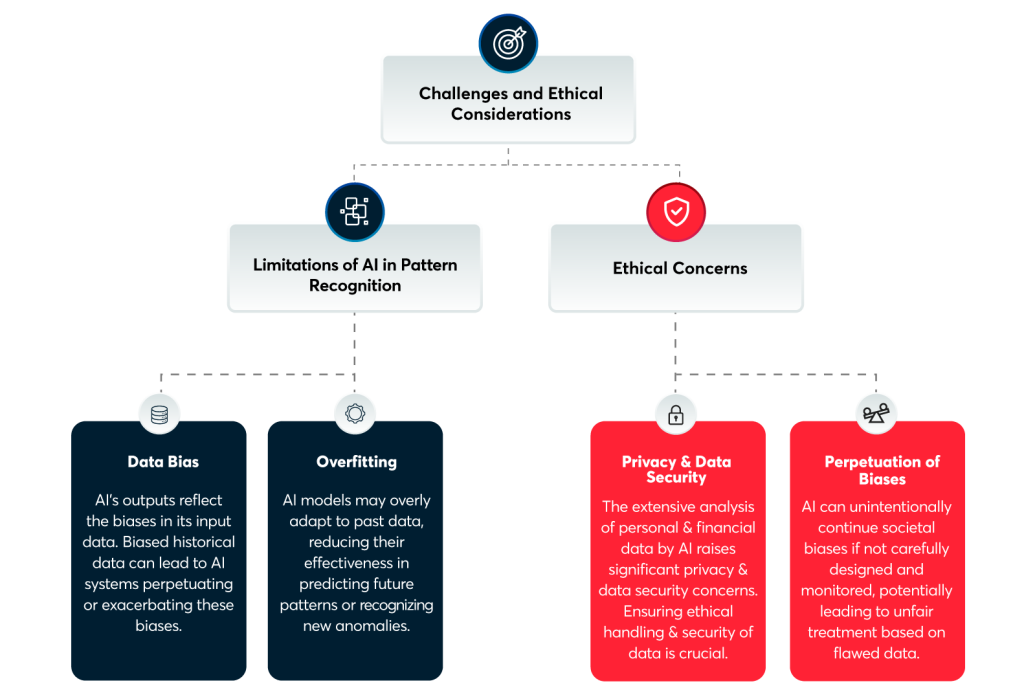
Commonly Faced Challenges in Fintech App Development
Security and Data Protection
Since fintech apps deal with sensitive financial information, security remains a top priority. Ensuring robust data encryption, secure authentication mechanisms, and protection against cyber threats require dedicated effort and expertise. Staying updated with evolving security standards and complying with data protection regulations can take time and effort. You can choose IT staff augmentation so a skilled team can look after such matters.
Regulatory Compliance
It is essential that fintech apps adhere to complex and ever-changing regulations, such as anti-money laundering (AML), know-your-customer (KYC), and data protection laws. Understanding and implementing the necessary compliance measures while maintaining a seamless user experience can be challenging.
Integration with Legacy Systems
More than often, fintech apps have to be integrated with legacy systems within financial institutions. Legacy systems may have outdated technologies, complex data structures, and limited APIs, making integration challenging. Ensuring compatibility, data consistency, and secure communication between the app and legacy systems can be difficult, so enterprise application integration becomes all the more critical.
Scalability and Performance
To accommodate growing bases, the app must be capable of handling high volumes of transactions and scaling to accommodate growing user bases. Designing and implementing a scalable architecture, optimizing performance, and ensuring responsiveness under heavy loads are critical challenges in FinTech app development.
User Trust and Adoption
Building trust in the app’s security, reliability, and ability to handle financial transactions is crucial. Overcoming user skepticism, demonstrating compliance with regulations, and addressing data privacy and protection concerns are ongoing challenges. Additionally, encouraging user adoption and engagement amidst competition in the fintech market can be demanding.
Complex User Flows and Functionality
Fintech apps often involve intricate user flows due to the complexity of financial operations. Balancing the need for a streamlined user experience with the inclusion of comprehensive functionality can be challenging. Ensuring usability and simplicity while providing advanced financial features can be a delicate balance.
Evolving Technological Landscape
The fintech industry is rapidly evolving, with emerging technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) having a significant impact. Keeping up with these technological advancements, evaluating their applicability, and integrating them effectively into fintech apps can be a challenge.
Continuous Compliance and Regulatory Updates
Regulatory requirements and compliance standards are subject to frequent updates. Ensuring that the app remains compliant with changing regulations and implementing necessary updates can be a continuous challenge for FinTech app developers.
User Education and Support
Fintech apps often introduce users to new financial concepts, features, and processes. Providing effective user education, intuitive onboarding, and comprehensive support channels to address user queries and concerns can be challenging.
Rapid Time-to-Market
Fintech is a competitive industry, and time-to-market can be a critical factor for success. Developing fintech apps quickly while maintaining quality, security, and compliance can prove hectic, requiring efficient project management, resource allocation, and development and testing methodologies.
How to Develop a Fintech App with the Best Practices?
To make sure that you build Fintech apps with maximum efficiency, the following best practices can be considered.
A Security-First Approach
Prioritize security throughout the entire development process. Implement secure coding practices, encryption protocols, and strict access controls to protect user data. Regularly update and patch security vulnerabilities and conduct thorough security testing and audits.
Compliance with Regulations
Understand and comply with relevant regulatory frameworks and industry standards, such as data protection laws, and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, and know your customer (KYC) requirements. Keep abreast of changes in regulations and update the app accordingly.
User-Centric Design
Focus on delivering a seamless and intuitive user experience (UX) by understanding the needs and preferences of your target users. Conduct user research, usability testing, and iterate on the design to optimize usability and accessibility.
Performance Optimization
Optimize the app’s performance to ensure fast response times, smooth navigation, and efficient use of system resources. You can employ caching, lazy loading, and code optimization techniques to enhance app performance and minimize latency.
Scalability and Reliability
Design the app with scalability in mind to accommodate growing user bases and increasing transaction volumes. Use scalable infrastructure, employ load balancing, and conduct stress testing to ensure the app can handle peak loads without performance degradation.
Robust Backend Architecture
Build a reliable and scalable backend infrastructure to handle complex financial operations. Employ microservices or modular architecture to promote code reusability, scalability, and ease of maintenance. Ensure proper data storage and backup mechanisms to prevent data loss.
Secure Authentication and Authorization
Implement strong user authentication mechanisms, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), biometric authentication, or OAuth/OpenID Connect protocols. Follow secure session management practices and enforce strong password policies.
Regular Testing and Quality Assurance
Conduct comprehensive testing at all stages of development, including functional testing, integration testing, security testing, and performance testing. Employ both manual and automated testing techniques to identify and address issues promptly.
Continuous Monitoring and Updates
Monitor the app’s performance, security, and user feedback continuously. Employ analytics tools and monitoring systems to track app usage, identify potential issues, and gather user insights. Regularly release updates and bug fixes to enhance app functionality and address user feedback.
Collaboration with Industry Experts
Engage with professionals with expertise in fintech app development, security, and compliance. Seek advice from legal and regulatory experts to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Transparent Communication and Data Privacy
Maintain transparent communication with users regarding data usage, security practices, and privacy policies. Obtain explicit user consent for data collection and inform users about their rights and how their information is used.
Regular Audits and Security Assessments
Conduct periodic security audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing to identify and address potential security weaknesses. Engage third-party security experts to assess the app’s security posture.
Conclusion – Fintech is a Growing Domain You Cannot Ignore
The shift to online payments has grown exponentially, especially in the post-pandemic world. Businesses that need to update their payment methods and have not yet done so remain at a disadvantage, as users prioritize convenience in payments offered by fintech apps.
To get started with fintech, or augment your existing financial solutions, partner with a fintech app development company like VentureDive, which has an extensive portfolio and experience working in this domain.
FAQs related to Fintech App Development
Technologies used in fintech app development include:
- Mobile app development frameworks (e.g., React Native, Flutter) for building cross-platform applications.
- Backend technologies (e.g., Node.js, Python) to handle server-side logic, data storage, and integration with external systems.
- Secure communication protocols (e.g., HTTPS, SSL) to ensure data encryption and secure transmission.
- Financial institutions and service providers provide APIs and SDKs for integrating features like payments, account aggregation, or investment tools.
The development timeline to create a fintech app depends on its complexity, features, development approach, and the size of the development team. Depending on the complexity of the features, it can range from a few months to more than a year.
Fintech app development costs depend on factors such as the project’s scope, features, development hours, and the development team’s rates. Complex fintech apps with advanced functionalities may have higher development costs than simpler applications.